MESMco4 | Discuss the terms True Stress and Natural Strain |
MASap1 | Employ material constitutive data appropriately in analysis and simulation. |
MASco15 | If relevant to your industry sector, explain how use of a modulus and allowable stress can be used in a small displacement linear elastic analysis of a plastic component. |
MASco9 | Explain, in metallurgical terms, how brittle and ductile cracks form in steels and how their appearances differ. |
MASco5 | Discuss the relationship between transition temperature and toughness and ductility. |
MASkn4 | List any material temperature limits (high and low) specified for the materials commonly used in your industry sector. |
FATkn4 | Sketch a sinusoidal stress variation and show the maximum stress, minimum stress, mean stress, alternating stress (or stress amplitude), stress range and stress ratio. |
FATkn3 | List potential sites for fatigue in your company products. |
FATkn6 | List ways of inducing beneficial compressive stresses in your company products. |
FATco1 | Discuss the initiation, propagation and fast fracture stages of Fatigue in metallic materials. |
FATco2 | Describe how the data used to construct an S-N curve are obtained. |
FATco3 | Discuss the term high cycle fatigue, highlighting a common source in your company products. |
FATco4 | Discuss the statistical nature of fatigue and explain how this is handled in relevant design standards and codes of practice. |
FATco5 | Discuss the salient features of an S-N diagram for steels and explain the terms endurance limit, infinite life and low cycle fatigue. |
FATco7 | Discuss the observed relationship between endurance limit and static tensile strength for steels and explain why this relationship does not hold for welded steels. |
FATco10 | Contrast the Stress-Life and Strain Life / Manson-Coffin approaches to fatigue assessment. |
FATco11 | Explain the use of Endurance Limit Modifying Factors in Stress-Life based fatigue assessment. |
FATco12 | Discuss how temperature, plate thickness and modulus effects are typically handled in relevant design standards and codes of practice and explain why this is necessary. |
FATco14 | Discuss the term Fatigue Strength Reduction Factor in relation to stress concentrations and explain how this has traditionally been handled in relevant design standards and codes of practice. |
FATco15 | Discuss the concept of cumulative damage and explain how this is commonly handled. |
FATco16 | Explain why a multiaxial stress field can complicate an analysis and discuss approaches to handling this. |
FATco17 | Discuss the significance of the choice of equivalent stress used in the fatigue assessment of welded joints |
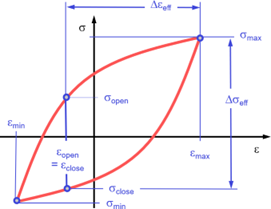
FATco29 | Explain how a Cyclic Stress-Strain Curve is constructed and used. |
FATco30 | Explain Neuber's Rule and its limitations and why corrections to the elastic strain range from an elastic analysis may be necessary. |
FATco36 | Discuss any particular characteristic fatigue properties and behaviour for any materials being considered in analyses and assessment. |
FATco37 | Reflect on how variable amplitude load sequencing can affect the prediction of damage accumulation and fatigue life. |
FATap2 | Carry out elastic fatigue assessment using design standards and code guidelines for components and structures including any special procedures for ancillary components such as bolts, |
FATap3 | Modify the results of an elastic analysis for the effects of plasticity, where necessary. |
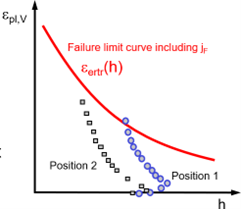
FATap4 | Conduct plastic analyses as necessary, to evaluate equivalent plastic strain ranges in components and assess using design standards and code guidelines. |
FATap5 | Use Reservoir Counting / Rainflow Method or similar to specify the necessary stress ranges, number of cycles and loading history for any component to be analysed. |
FATap6 | Employ a finite element analysis system for the fatigue analysis of a component or structure. |
PLASev3 | Assess the significance of neglecting any feature or detail in any nonlinear material idealisation. |
PLASsy1 | Specify the use of elastic perfectly plastic and bi-linear or multi-linear hardening constitutive data as appropriate. |
PLASap2 | Use FEA to determine Limit Loads for a range of components. |
PLASap7 | Using standard material data, derive a true stress vs true strain curve to be used for nonlinear analysis. |
PLASco21 | Explain the rationale behind the 5% strain limit in some codes of practice. |
PLASco26 | Discuss approaches employed to improve the finite element prediction of limit load. |
PLASco33 | Explain Neuber's Rule. |